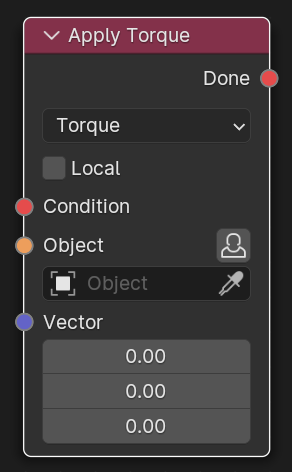
Apply Torque
Rotates an object using torque mechanics and tries to follow real-world physical rules. It uses the Newton-meter as a unit of measure (torque = force x length of the lever).
In the real world, applying torque requires a lever with length and an object that is experiencing a binding force. For movement to take place on this object the torque must be greater than the bonding force. The real bonding force generally encompasses friction and tension.
Unlike in the real world, where the wrench holds the screw that is being rotated, in the UPBGE there is no such limitation and so all torque force is applied at once, which can perpetuate the rotation continuity.
If the object has some kind of Collision Bounds different from sphere, it will need a torque value greater than the force that makes the object static.
Tip
In order to limit pivoting of the torque, assign a rotation limit to a certain origin with either an Armature Bone or a Rigid Body Joint Constraint.
Properties
- Mode
Selected mode of operation to apply.
- Local
If checked, Torque will be applied following the object’s local axes, else global axes.
Input
- Condition
The condition for this node to start.
- Object
Object that will be rotated.
- Vector
The value that will be applied to the rotation in Newton-meters.
Output
- Done
True if the node performed successfully, else False.